Professional solutions on concrete addtives, Concrete Foaming Agent, Superplasticizer, CLC Blocks Additives, and foaming machine
Hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC) is a polymer widely used in various industries such as pharmaceuticals, food, and construction. Its unique properties, such as water solubility, thickening, and film-forming ability, make it an indispensable material in many applications. This article delves into the chemistry and applications of HPMC, with a particular focus on its differences from carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC) and methods for identifying genuine HPMC.
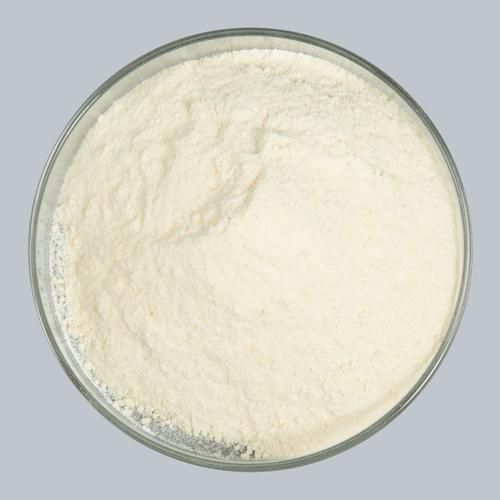

Hydroxypropyl methylcellulose
Hydroxypropyl methylcellulose, also known as hydroxypropyl methylcellulose, is a semi-synthetic, non-ionic, water-soluble polymer derived from cellulose. It is produced through the etherification reaction of cellulose with epichlorohydrin and chloromethane, resulting in a polymer with both hydroxyl and methoxy groups. The degree of substitution (DS) and molar substitution (MS) of these functional groups can be controlled during the synthesis process, allowing for the production of HPMC with customized properties.
The key characteristics of HPMC include
Water solubility: HPMC is highly soluble in cold water, making it easy to use in aqueous systems.
Thickening and viscosity control: It can increase the viscosity of the solution, providing excellent thickening and rheological control.
Film forming ability: HPMC forms a strong and flexible film when dried, which can be used for coating and packaging applications.
Stability: Stable within a wide pH range and resistant to microbial degradation.
Temperature sensitivity: some grades of HPMC have thermal gelling properties, forming gel at high temperatures, which can be used for controlled release preparations.
| Parameter | Value |
| Chemical Name | Hydroxypropyl Methylcellulose (HPMC) |
| CAS Number | 9004-65-3 |
| Molecular Formula | C<sub>8</sub>H<sub>15</sub>O<sub>6</sub>.x(C<sub>3</sub>H<sub>7</sub>O).y(CH<sub>3</sub>) (x and y are variable, indicating the degree of substitution) |
| Appearance | White to off-white powder |
| Odor | Odorless or with a slight characteristic odor |
| pH of 2% Solution | 6.0 – 8.0 (at 25°C) |
| Viscosity @ 2% Solution, 20°C | Varies widely depending on grade, typically from 3 mPa·s to 100,000 mPa·s |
| Substitution Degree (DS) | Typically 1.2 – 2.0 for methyl groups, 0.1 – 1.5 for hydroxypropyl groups |
| Moisture Content | ≤ 5.0% |
| Ash Content | ≤ 0.1% |
| Particle Size | 80 mesh (180 μm) through, 100% |
| Solubility in Water | Soluble in cold water, forms a clear to slightly hazy solution; insoluble in most organic solvents |
| Storage Conditions | Store in a cool, dry place. Keep container tightly closed. Avoid exposure to moisture and heat. |
| Shelf Life | 2 years when stored under recommended conditions. |
Product parameter table of Hydroxypropyl methylcellulose
The difference between HPMC and CMC
Although HPMC and carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC) are both cellulose derivatives, they have different properties and applications. Understanding these differences is crucial for selecting suitable materials for specific purposes.
Chemical structure:
HPMC: Derived from cellulose by etherification with epichlorohydrin and chloromethane, forming polymers with hydroxyl and methoxy groups.
CMC: A polymer derived from cellulose by esterification with chloroacetic acid, forming a carboxymethyl group.
Attribute:
Water solubility:
HPMC: Highly soluble in cold water, some grades have thermal gelling properties.
CMC: soluble in hot and cold water but more sensitive to salt and pH changes.
PH stability:
HPMC: Stable over a wide pH range from acidic to alkaline.
CMC: It is more easily degraded under acidic conditions, which limits its use in low pH environments.
Viscosity:
HPMC: Provides excellent thickening and viscosity control with a smooth, creamy texture.
CMC: It can also provide a good thickening effect but may produce a slight gel-like consistency
Film-forming ability:
HPMC: forms a strong, flexible film that is moisture-proof and has good barrier properties.
CMC: The formed film is more brittle and has lower moisture resistance
Given the widespread use of HPMC, there is a risk of encountering counterfeit or substandard products. To ensure the quality and authenticity of HPMC, various methods can be used:
Visual inspection: The true color of HPMC should be white to off-white, without visible impurities. The powder should have consistent particle size without clumping or agglomeration.
Solubility test: Dissolve a small amount of HPMC in cold water. True HPMC should be completely dissolved, forming a clear and uniform solution without any undissolved particles. If HPMC is marked as having thermal gel performance, please check whether it forms a gel when heated to the specified temperature.
Viscosity measurement: Use a viscometer to measure the viscosity of a solution prepared with HPMC. Compare the results with the manufacturer’s specifications. Significant deviations may indicate that the product is not qualified.
PH stability: Prepare the HPMC solution and adjust the pH value to different levels. Observe the stability and viscosity of the solution. True HPMC should remain stable and maintain its stability over a wide pH range.
Hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC) is a widely used and indispensable polymer in modern chemistry, with applications spanning multiple industries. Its unique properties, such as water solubility, thickening, and film-forming ability, make it the preferred choice for pharmaceuticals, food, construction, and personal care. Understanding the differences between HPMC and CMC, as well as the methods to identify genuine HPMC, is crucial for ensuring the quality and performance of the final product. By adopting rigorous testing and validation procedures, manufacturers can ensure that they use high-quality HPMC to obtain high-quality and reliable final products. As the demand for advanced materials continues to grow, the role of HPMC in these applications will only become more important, driving continuous improvement in its production and quality control.
Supplier
Cabr-Concrete is a supplier under TRUNNANO of Concrete Admixture with over 12 years of experience in nano-building energy conservation and nanotechnology development. It accepts payment via Credit Card, T/T, West Union and Paypal. TRUNNANO will ship the goods to customers overseas through FedEx, DHL, by air, or by sea. If you are looking for Hydroxypropyl methylcellulose, please feel free to contact us and send an inquiry.sales@cabr-concrete.com