Professional solutions on concrete addtives, Concrete Foaming Agent, Superplasticizer, CLC Blocks Additives, and foaming machine
(Foaming Agent and Cement)
The foaming agent used in concrete foam is commonly a detergent-based product, but there are also hydrolyzed protein agents. Foaming agent is generally diluted with a certain proportion of water, usually about a 1-to-40 ratio and mixed in with the foam concrete mix.
The interaction between the foaming agent and cement is a large part of how it forms. It is important to mix small 0.2mm or less particles immediately after foam creation and before it hardens. This helps to stabilise the bubbles and prevent them from leaking water.
It has been shown that the flexural strength and compressive strength of a foam concrete can be increased with the addition of a slag, especially when silica fume is added to the mixture. It also improves the water absorption and drying shrinkage behavior of foam concrete.
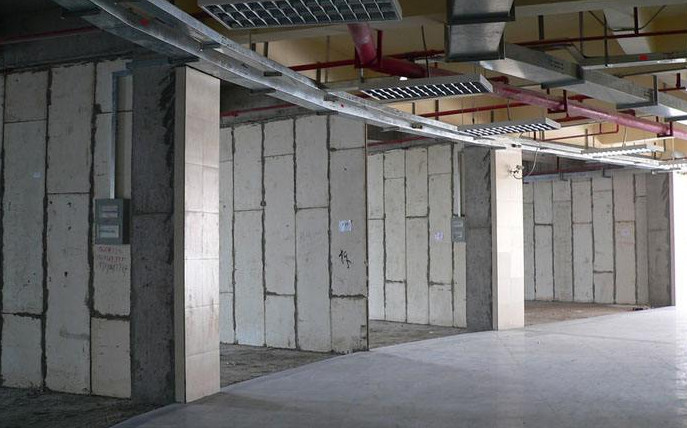
Workability properties of a foam concrete are directly related to the porosity of the mixture [51]. The pore structure of the aggregate type used affects the porosity of the foam concrete mixture. The use of RCA as fine aggregate in foam concrete increases the porosity and decreases the strength.
Drying shrinkage of a foam concrete can be reduced by using waste clay brick powder as an aggregate. Its pore size distribution is more narrow than that of silica sand and it can absorb more water.
The permeability of a foam concrete is controlled by the amount of water used in the slurry. The presence of too much water decreases the flexural strength and drying shrinkage, which can make it more difficult to construct.
(Foaming Agent and Cement)