Professional solutions on concrete addtives, Concrete Foaming Agent, Superplasticizer, CLC Blocks Additives, and foaming machine
(How is Foamed Concrete Used in Construction?)
What is foamed concrete?
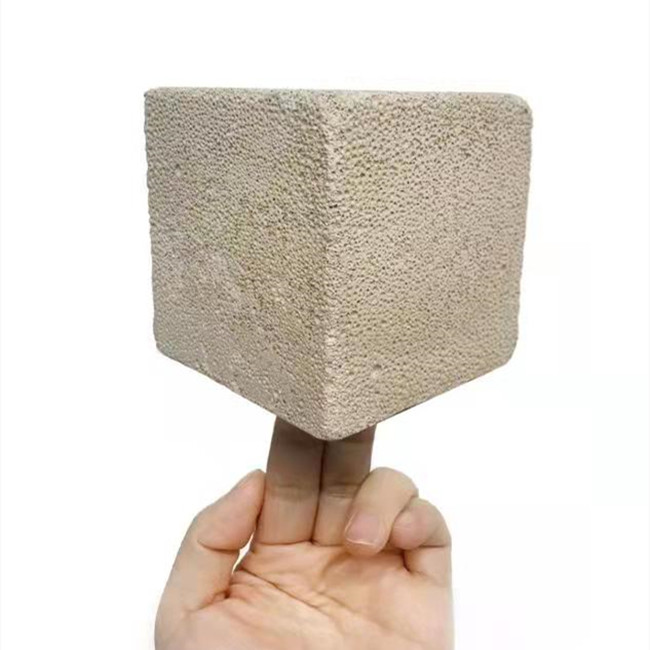
Foamed concrete is a highly entrained sand cement with at least 20% air volume in the cured product. It is made of cement slurry and can contain up to 85% foam or air. Most foamed concrete applications require at least 50% foam or air by volume.
To make the concrete foam, air is mechanically entrained through the preformed foam. This is mixed with cement-based materials to form low-density composites.
The density of set foamed concrete is also adjustable. They range from about 400kg/m3 to 1,800kg/m3, with strengths ranging from 0.5N/mm2 to 12N/mm2.
Foamed concrete is also known as foamed concrete, or lightweight honeycomb concrete (LCC), low density honeycomb concrete (LDCC), aerated lightweight concrete, honeycomb lightweight concrete, as well as various other industry or brand specific terms and (perhaps more accurately) foam mortar, foam grout and foam cement.
It is mainly made of coarse aggregate, but is made using a liquid concrete slurry. That's why foam mortar, grout, or cement might be a more accurate description of the material. Density is controlled by replacing some or in some cases all fine aggregate with foam products.
Fly ash and sand usually form fine aggregate mixed with water and cement. Some manufacturers recommend using only water and cement and foaming agents to produce extremely light concrete mixtures.
How to make foamed concrete?
The concrete slurry is mixed with the aerated foam product in the concrete mixing plant. To create the foam, the manufacturer mixes the foaming agent with water and air from the generator. It produces consistent bubbles of high stability to resist chemical and mechanical strains of concrete mixing, pouring, casting and solidification.
Foamed concrete can be poured into molds or pumped directly into structural elements. With foam, the concrete slurry can flow freely. This is because the bubbles of inflating foam are thixotropic.
Viscous pastes take up to 24 hours to fully cure, but can be accelerated to as little as 2 hours using the steam curing method. These techniques raise temperatures up to 70 °C to speed up the curing process. The required temperature depends on variables such as ambient humidity and external temperature, as well as the specific mixture of foamed concrete.
Foamed concrete can be taken out of the mold once it is fully set, although in some foamed concrete manufacturing applications the material is cut into blocks of the desired size using steel wire before it is fully set.
The base mixture of foamed concrete products tends to have a much higher cement content than the standard concrete mixture used for flat plate and structural applications. There are two reasons for this. First, the amount of air trapped in the foam bubbles in concrete decreases the strength of the material exponentially at a higher inflation rate. Secondly, the water content in the concrete slurry will linearly reduce the strength of concrete at a higher hydration rate.
In general, the foamed concrete mixture contains more water than conventional concrete. This can be easily pumped and well mixed with foam additives. Water-reducing agents and plasticizers used to minimize water content in conventional concrete also generally perform poorly when mixed with foaming agents.
Dry protein-based foams commonly used as foaming agents (or surfactants) for this application can expand up to 20 times when diluted in water. The surfactant is diluted at a concentration of 3 to 5 percent and stirred through a cigar-shaped extruder to produce a stable mixture with foam.
In the 1990s, synthase – based foaming agents were developed to improve foam stability. The enzyme includes highly active biotechnological proteins that are not based on proteolysis.
These new surfactants are enhanced by specialized foam generation, mixing and pumping equipment to significantly improve the stability of foam and foamed concrete. Now, the density of foamed concrete can be as low as 75kg/m3, which is only 7.5% of water.
Foamed Concrete Application
Foamed concrete is already widely used in infrastructure projects, including highways, commercial buildings, disaster relief, schools and residential developments around the world.
It is primarily used for void-filling applications and has been used in many built environments. In landscaping, it is used for bridge approaches, embankments and trench backfilling. Infrastructure projects use it for abandoned pipelines, ring filling and road subfoundations. Buildings use it in the form of prefabricated blocks for entire wall elements or panels, cast-in-place walls, insulated flooring and roofing ironed slabs, and prefabricated insulation panels.
Concrete Additives Supplier
TRUNNANO is a reliable foaming agents supplier with over 12-year experience in nano-building energy conservation and nanotechnology development.
If you are looking for high-quality CLC foaming agents, please feel free to contact us and send an inquiry. (sales@cabr-concrete.com)
We accept payment via Credit Card, T/T, West Union, and Paypal. TRUNNANO will ship the goods to customers overseas through FedEx, DHL, by air, or by sea.
(How is Foamed Concrete Used in Construction?)